ASEAN, China, Other Partners Sign World’s Biggest Trade Pact
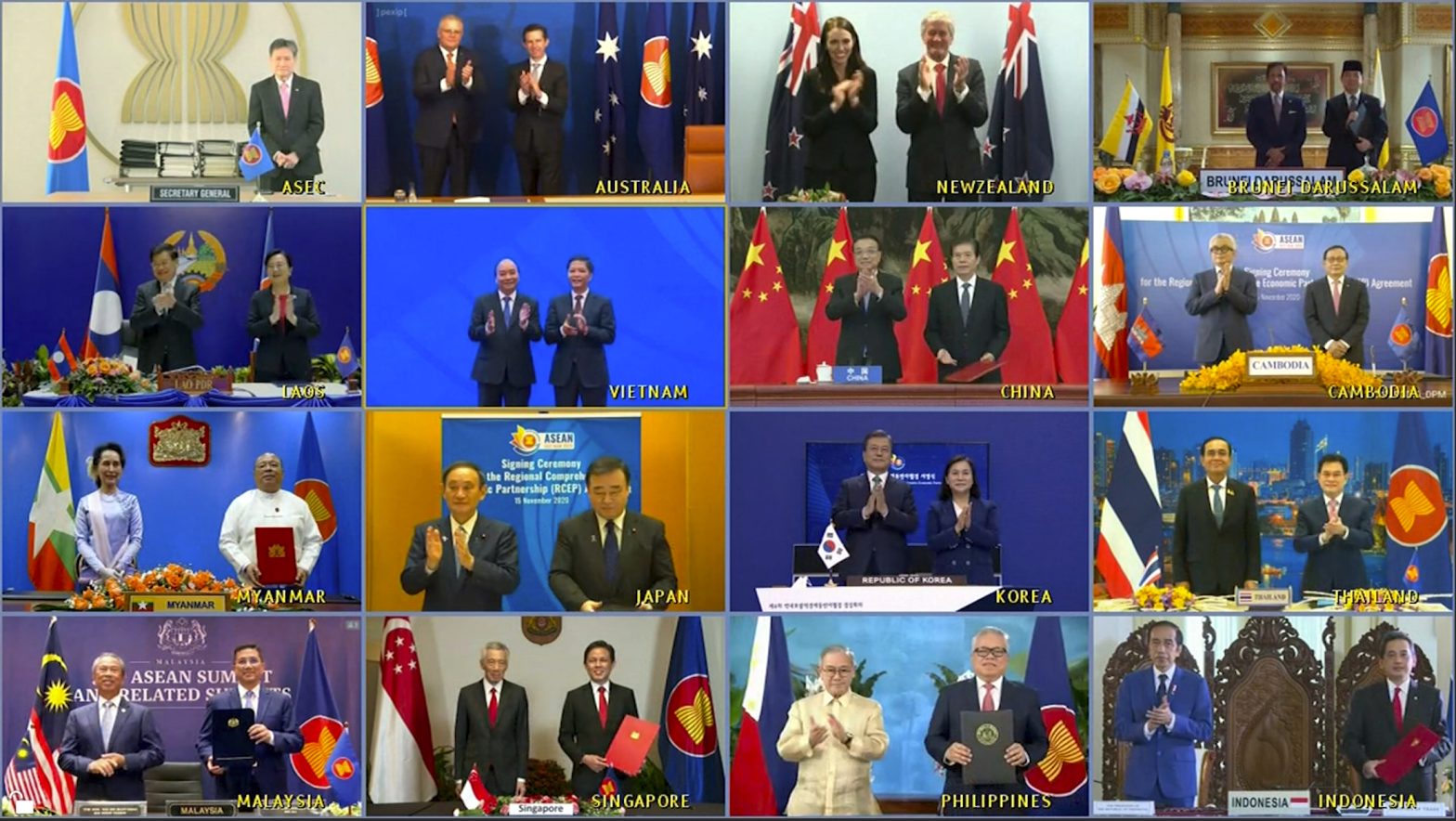

China and 14 other countries agreed Sunday to set up the world’s largest trading bloc, encompassing nearly a third of all economic activity, in a deal many in Asia are hoping will help hasten a recovery from the shocks of the pandemic.
The Regional Comprehensive Economic Partnership, or RCEP, was signed virtually on Sunday on the sidelines of the annual summit of the 10-nation Association of Southeast Asian Nations.
“I am delighted to say that after eight years of hard work, as of today, we have officially brought RCEP negotiations to a conclusion for signing,” said host country Vietnam’s prime minister, Nguyen Xuan Phuc.
“The conclusion of RCEP negotiation, the largest free trade agreement in the world, will send a strong message that affirms ASEAN’s leading role in supporting the multilateral trading system, creating a new trading structure in the region, enabling sustainable trade facilitation, revitalizing the supply chains disrupted by COVID-19 and assisting the post-pandemic recovery,” Phuc said.
The accord will take already low tariffs on trade between member countries still lower, over time, and is less comprehensive than an 11-nation trans-Pacific trade deal that President Donald Trump pulled out of shortly after taking office.
Apart from the 10 ASEAN members, it includes China, Japan, South Korea, Australia and New Zealand, but not the United States. Officials said the accord leaves the door open for India, which dropped out due to fierce domestic opposition to its market-opening requirements, to rejoin the bloc.
It will take time to fully assess exact details of the agreement encompassing tariff schedules and rules for all 15 countries involved — the tariffs schedule just for Japan is 1,334 pages long.
It is not expected to go as far as the European Union in integrating member economies but does build on existing free trade arrangements.
The deal has powerful symbolic ramifications, showing that nearly four years after Trump launched his “America First” policy of forging trade deals with individual countries, Asia remains committed to multi-nation efforts toward freer trade that are seen as a formula for future prosperity.
Ahead of Sunday’s RCEP “special summit” meeting, Japanese Prime Minister Yoshihide Suga said he would firmly convey his government’s support for “broadening a free and fair economic zone, including a possibility of India’s future return to the deal, and hope to gain support from the other countries.”
The accord is also a coup for China, by far the biggest market in the region with more than 1.3 billion people, allowing Beijing to cast itself as a “champion of globalization and multilateral cooperation” and giving it greater influence over rules governing regional trade, Gareth Leather, senior Asian economist for Capital Economics, said in a report.
China’s official Xinhua News Agency quoted Premier Li Keqiang hailing the agreement as a victory against protectionism, in remarks delivered via a video link.
“The signing of the RCEP is not only a landmark achievement of East Asian regional cooperation, but also a victory of multilateralism and free trade,” Li said.
The agreement is expected to help China, Japan and South Korea finally reach a trilateral free trade deal after years of struggling to bridge their differences.
Now that Trump’s opponent Joe Biden has been declared president-elect, the region is watching to see how U.S. policy on trade and other issues will evolve.
Analysts are skeptical Biden will push hard to rejoin the trans-Pacific trade pact or to roll back many of the U.S. trade sanctions imposed on China by the Trump administration given widespread frustration with Beijing’s trade and human rights records, and accusations of spying and technology theft.
Critics of free trade agreements say they tend to encourage companies to move manufacturing jobs overseas. So, having won over disaffected rust-belt voters in Michigan and western Pennsylvania in the Nov. 3 election, Biden is “not going to squander that by going back into TPP,” Michael Jonathan Green of the Center for Strategic and International Studies said in a web seminar.
But given concerns over China’s growing influence, Biden is likely to seek much more engagement with Southeast Asia to protect U.S. interests, he said.
The fast-growing and increasingly affluent Southeast Asian market of 650 million people has been hit hard by the pandemic and is urgently seeking fresh drivers for growth.
RCEP originally would have included about 3.6 billion people and encompassed about a third of world trade and global GDP. Minus India, it still covers more than 2 billion people and close to a third of all trade and business activity.
The United States-Mexico-Canada Agreement, or USMCA, the retooled version of the North American Free Trade Agreement under Trump, covers slightly less economic activity but less than a tenth of the world’s population. The EU and Comprehensive and Progressive Trans-Pacific Partnership, the revised version of the deal Trump rejected, also are smaller. RCEP includes six of the 11 remaining CPTPP members.
India balked at exposing its farmers and factories to more foreign competition. Among other concerns, Indian dairy farmers are worried about competition from New Zealand and Australian milk and cheese producers. Automakers fear imports from across the region. But overall the biggest fear is over a flood of manufactured goods from China.
Trade and investment flows within Asia have vastly expanded over the past decade, a trend that has accelerated amid feuding between the U.S. and China, which have imposed billions of dollars’ worth of punitive tariffs on each other’s exports.
The RCEP agreement is loose enough to stretch to fit the disparate needs of member countries as diverse as Myanmar, Singapore, Vietnam and Australia. Unlike the CPTPP and EU, it does not establish unified standards on labor and the environment or commit countries to open services and other vulnerable areas of their economies.
But it does set rules for trade that will facilitate investment and other business within the region, Jeffrey Wilson, research director at the Perth USAsia Center, said in a report for the Asia Society.
“RCEP, therefore, is a much-needed platform for the Indo-Pacific’s post-COVID recovery,” he wrote.
ASEAN members include Cambodia, Indonesia, Laos, Myanmar, the Philippines, Thailand, Brunei, Singapore, Malaysia and Vietnam.
___
Associated Press writers Hau Dinh in Hanoi, Vietnam, and Mari Yamaguchi in Tokyo contributed to this report.