What You Need to Know About Dietary Supplements

WASHINGTON — Have you ever ventured down the supplement aisle at a health food store and wondered what you’re missing? With all kinds of powders and capsules on the market that promise to improve your health, it’s tempting to try one out.
Here, we’ll provide some background on common types of supplements, how to know if you need one, safety tips to keep in mind and natural alternatives.
Common Types of Supplements and Vitamins
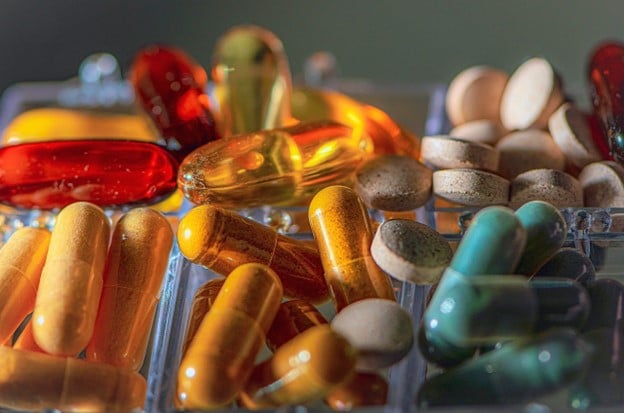
Dietary supplements are what they say they are — they’re meant to supplement or add to your regular diet. They may contain vitamins, minerals, herbs, botanicals, amino acids, enzymes and other ingredients. They typically come in powder, capsule, gummy, or liquid form.
Some supplements are popular for athletic performance, some for general health and others may improve sleep or reduce stress.
Athletic Powders:
Gym-goers often reach for supplements to support their fitness goals.
- Protein Powder: Protein powder can help you reach your protein intake goals, typically by adding it to water or a smoothie. Protein is essential for building muscle and recovering from exercise. Protein powder lacks important micronutrients and is not meant to replace food protein sources.
- Creatine Power: Creatine is an amino acid that may help you build muscle and increase strength when you pair it with a consistent resistance training program, like weightlifting.
- Pre-Workout Powder: Pre-workout is generally a blend of caffeine and amino acids that can boost energy and focus before exercise.
- Electrolyte Powder: Electrolytes are essential minerals including sodium, potassium, chloride, magnesium and others that can help you rehydrate if you exercise for many hours at a high intensity in the heat.
Other Powders:
- Greens Powder: Greens powders typically contain a blend of fruits, vegetables and antioxidants in a concentrated powder form. Mix it with water to boost your veggie intake, but it’s not a replacement for eating whole fruits and vegetables.
- Fiber Powder: If you don’t get enough fiber in your diet, a fiber powder may help improve your digestive health.
Vitamins and Minerals:
Now, we’ll move on to vitamins and minerals — usually in capsule or pill form.
- Multivitamins: A multivitamin can be anything, really, but typically contains a blend of vitamins and nutrients. They’re often marketed to different genders and age groups.
- Vitamins A, B-Complex, C, D, K, E: You can get your alphabet vitamins individually.
- Calcium: Calcium helps support bone health.
- Iron: Iron supports blood health and oxygen transport. Iron deficiencies are common in women.
- Magnesium: Magnesium is a mineral that supports muscle and nerve health and energy production. Magnesium supplements may improve sleep and reduce stress.
- Omega-3 Fatty Acids: Omega-3s can be found in various supplements, and fish oil is a popular one. It may support joint and brain health.
- Zinc: Zinc may help enhance your immune system.
Stress, Sleep, and Digestion
- GABA: GABA stands for gamma-aminobutyric acid. It’s an amino acid and neurotransmitter that may help reduce stress and improve sleep.
- Melatonin: Melatonin is a hormone that helps regulate your sleep and wake cycle. In supplement form, it may help improve sleep.
- Prebiotics and Probiotics: Prebiotics and probiotics may help support digestive health.
When to Take Them
Health professionals recommend reaching your daily nutrient needs through whole foods. Supplements may help when you need extra.
- Nutrient Deficiencies and Malabsorption: Getting a blood test from your doctor is the only way to know if you need a dietary supplement. Certain medical conditions may also prevent your body from absorbing nutrients from your diet.
- Athletic Performance: Though supplements aren’t necessary for athletic performance, many regular fitness enthusiasts and athletes take them to support their goals.
- Immune System Support: Taking Vitamin C and Zinc in colder months is common to help strengthen your immune system.
Judging Safety and Natural Alternatives
Dietary supplements are not regulated by the FDA. They do not need to be guaranteed to be safe or effective to be sold. Some additives or ingredients in supplements (like sweeteners) may be “generally regarded as safe” by the FDA. However, the FDA does not deem any full dietary supplement product as safe or not.
When choosing a dietary supplement, read the ingredients and warnings. Picking something that seems to contain more natural ingredients may help, but still isn’t a guarantee of safety. Check with your doctor before trying a new supplement. Some may interact with the medications you take or conditions you have. Dietary supplements may also cause side effects.
Be wary of supplements that promise to cure, treat, or prevent a disease — these are illegal and should be classified as drugs.
Try your best to get all the vitamins, minerals and nutrients you need by eating a balanced diet filled with colorful fruits and vegetables, whole grains, lean protein sources, fish, and dairy products. (Or plant-based alternatives, if you’re a vegetarian or vegan). Plus, drink plenty of water.
Necessary or Not?
None of these products are truly necessary for a healthy life — unless you’ve been diagnosed with a deficiency or medical condition and could use extra nutrients. Always consult with your doctor before trying a new product.
Our website content, services and products are for informational purposes only. The Well News does not provide medical advice, diagnosis or treatment. If you have medical concerns or questions, discuss with your health care professional.
You can reach us at [email protected] and follow us on Facebook and X (formerly known as Twitter)