Study: Already Shrunk by Half, Swiss Glaciers Melting Faster
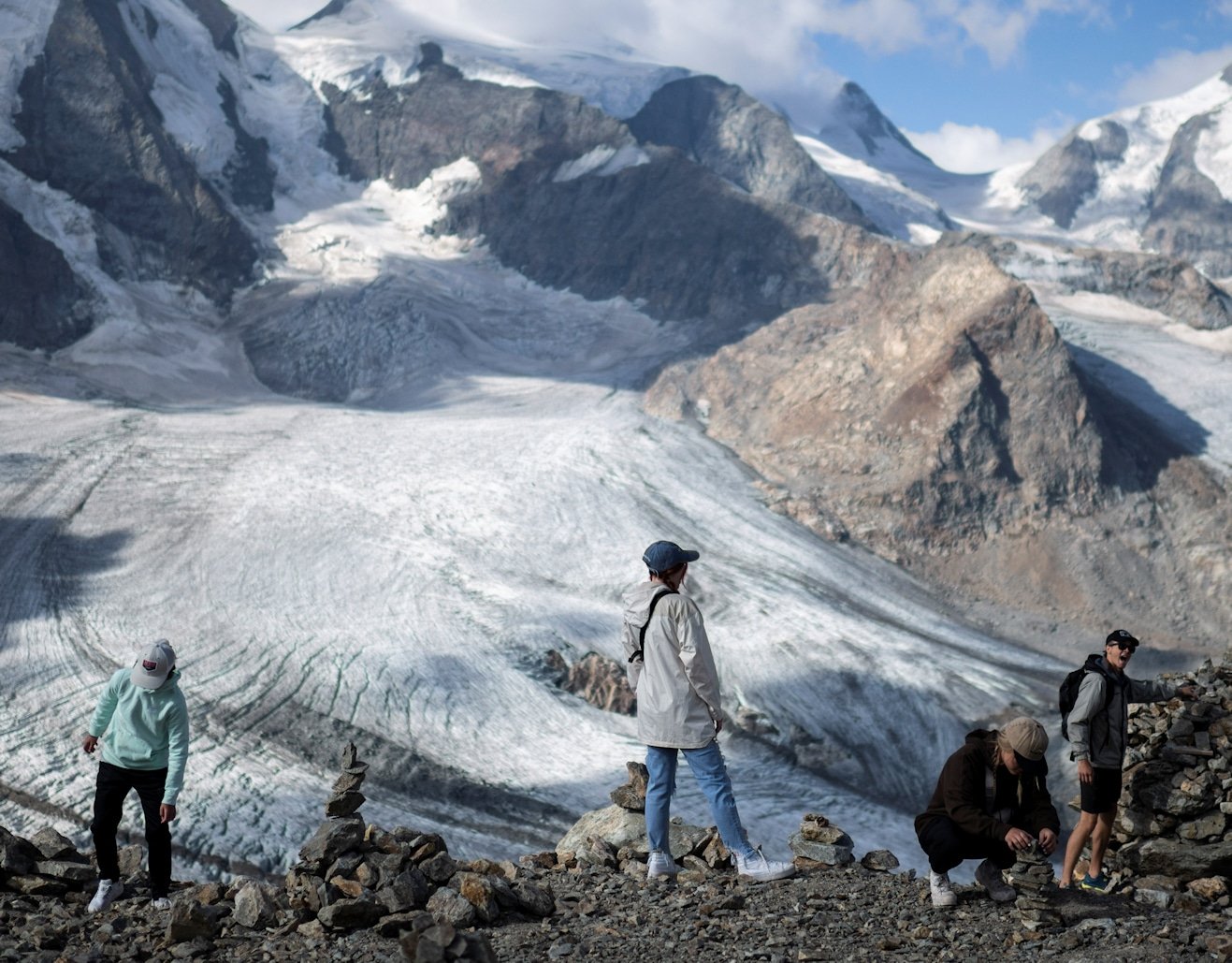

GENEVA (AP) — Switzerland’s 1,400 glaciers have lost more than half their total volume since the early 1930s, a new study has found, and researchers say the ice retreat is accelerating at a time of growing concerns about climate change.
ETH Zurich, a respected federal polytechnic university, and the Swiss Federal Institute on Forest, Snow and Landscape Research on Monday announced the findings from a first-ever reconstruction of ice loss in Switzerland in the 20th century, based in part on an analysis of changes to the topography of glaciers since 1931.
The researchers estimated that ice volumes on the glaciers had shrunk by half over the subsequent 85 years — until 2016. Since then, the glaciers have lost an additional 12%, over just six years.
“Glacier retreat is accelerating. Closely observing this phenomenon and quantifying its historical dimensions is important because it allows us to infer the glaciers’ responses to a changing climate,” said Daniel Farinotti, a co-author of the study, which was published in scientific journal The Cryosphere.
By area, Switzerland’s glaciers amount to about half of all the total glaciers in the European Alps.
The teams drew on a combination of long-term observations of glaciers. That included measurements in the field and aerial and mountaintop photographs — including 22,000 taken from peaks between the two world wars. By using multiple sources, the researchers could fill in gaps. Only a few of Switzerland’s glaciers have been studied regularly over the years.
The research involved using decades-old techniques to allow for comparisons of the shape and position of images of terrain, and the use of cameras and instruments to measure angles of land areas. The teams compared surface topography of glaciers at different moments, allowing for calculations about the evolution in ice volumes.
Not all Swiss glaciers have been losing ice at the same rates, the researchers said. Altitude, amounts of debris on the glaciers, and the flatness of a glacier’s “snout” — its lowest part, which is the most vulnerable to melting — all affect the speeds of ice retreat.
The researchers also found that two periods — in the 1920s and the 1980s — actually experienced sporadic growth in glacier mass, but that was overshadowed by the broader trend of decline.
The findings could have broad implications for Switzerland’s long-term energy sources, since hydropower produces nearly 60% of the country’s electricity, according to government data.