Colorado River Cuts Expected for Arizona, Nevada and Mexico

SALT LAKE CITY (AP) — The federal government on Tuesday is expected to announce water cuts to states that rely on the Colorado River as drought and climate change leave less water flowing through the river and deplete the reservoirs that store it.
The Colorado River provides water to 40 million people across seven states in the American West as well as Mexico and helps feed an agricultural industry valued at $15 billion a year. Cities and farms across the region are anxiously awaiting official hydrology projections — estimates of future water levels in the river — that will determine the extent and scope of cuts to their water supply.
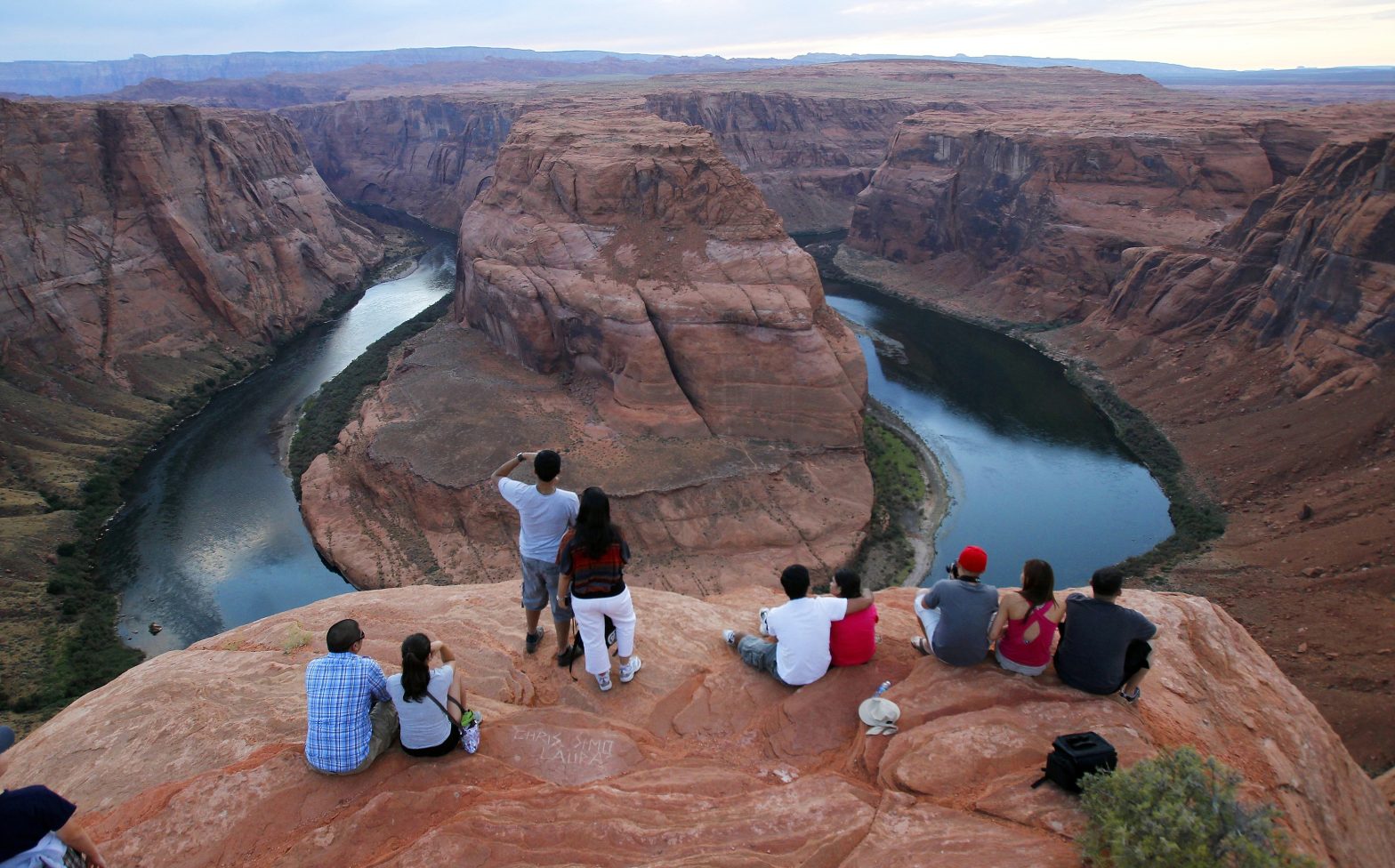
Water officials in Arizona, California, Colorado, Nevada, New Mexico, Utah and Wyoming are expecting federal officials to project Lake Mead — located on the Nevada-Arizona border and the largest manmade reservoir in the U.S. — to shrink to dangerously low levels that could disrupt water delivery and hydropower production and cut the amount of water allocated to Arizona and Nevada, as well as Mexico.
And that’s not all: Officials from the states are also scrambling to meet a deadline imposed by the U.S. Bureau of Reclamation to slash their water use by at least 15% in order to keep water levels at the river’s storage reservoirs from dropping even more.
Together, the projections and the deadline for cuts are presenting Western states with unprecedented challenges and confronting them with difficult decisions about how to plan for a drier future.
While the Bureau of Reclamation is “very focused on just getting through this to next year,” any cutbacks will likely need to be in place far longer, said University of Oxford hydrologist Kevin Wheeler.
“What contribution the science makes is, it’s pretty clear that that these reductions just have to have to stay in place until the drought has ended or we realize they actually have to get worse and the cuts have to get deeper,” he said.
The cuts expected to be announced Tuesday are based on a plan the seven states as well as Mexico signed in 2019 to help maintain reservoir levels. Under that plan, the amount of water allocated to states depends on the water levels at Lake Mead. Last year, the lake fell low enough for the federal government to declare a first-ever water shortage in the region, triggering mandatory cuts for Arizona and Nevada as well as Mexico in 2022.
Officials expect hydrologists will project the lake to fall further, triggering additional cuts to Nevada, Arizona and Mexico next year. States with higher priority water rights are not expected to see cuts.
Reservoir levels have been falling for years — and faster than experts predicted — due to 22 years of drought worsened by climate change and overuse of the river. Scorching temperatures and less melting snow in the spring have reduced the amount of water flowing from the Rocky Mountains, where the river originates before it snakes 1,450 miles (2,334 kilometers) southwest and into the Gulf of California.
Already, extraordinary steps have been taken this year to keep water in Lake Powell, the other large Colorado River reservoir, which sits upstream of Lake Mead and straddles the Arizona-Utah border. Water from the lake runs through Glen Canyon Dam, which produces enough electricity to power between 1 million and 1.5 million homes each year.
After water levels at Lake Powell reached levels low enough to threaten hydropower production, federal officials said they would hold back an additional 480,000 acre-feet (more than 156 billion gallons or 592 million cubic meters) of water to ensure the dam could still produce energy. That water would normally course to Lake Mead.
Under Tuesday’s reductions, Arizona is expected to lose slightly more water than it did this year, when 18% of its supply was cut. In 2023, it will lose an additional 3%, an aggregate 21% reduction from its initial allocation. Farmers in central Arizona will largely shoulder the cuts, as they did this year.
Mexico is expected to lose 7% of the 1.5 million acre-feet it receives each year from the river. Last year, it lost about 5%. The water is a lifeline for northern desert cities including Tijuana and a large farm industry in the Mexicali Valley, just south of the border from California’s Imperial Valley.
Nevada is also set to lose water — about 8% of its supply — but most residents will not feel the effects because the state recycles the majority of its water used indoors and doesn’t use its full allocation. Last year, the state lost 7%.
__
Naishadham reported from Washington. The Associated Press receives support from the Walton Family Foundation for coverage of water and environmental policy. The AP is solely responsible for all content. For all of AP’s environmental coverage, visit https://apnews.com/hub/climate-and-environment