Study Identifies ‘Creature’ That Promotes Tooth Decay
An international team of researchers has identified a “creature” that thrives on sugar, lunges at tooth-like surfaces and is especially skilled at promoting tooth decay.
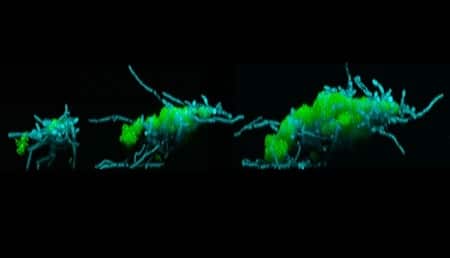
The so-called “superorganism” is actually composed of cavity-causing bacteria that piggyback on fungi, enabling it to walk from tooth to tooth and spread faster and farther than either organism alone.
The findings were published in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences.
“This is not something I would even dream about,” said co-senior author Hyun (Michel) Koo, D.D.S., Ph.D., a professor of orthodontics at the University of Pennsylvania, in a written statement.
Koo co-led the research with Knut Drescher, Ph.D., an associate professor at the University of Basel in Switzerland.
“These organisms from different kingdoms are nonmotile, meaning they can’t move by themselves. But when together, they develop mobility that’s usually reserved for higher organisms such as insects and vertebrates,” he said.
The researchers discovered the cross-kingdom assemblages in the saliva of young children with severe tooth decay. In lab experiments, real-time imaging revealed that the microbial clusters move across tooth-like surfaces by using the fungi’s fiber-like hyphae as “legs.”
As the hyphae elongate, they push against the surface, thrusting the cluster up and forward in a manner that resembles walking and lunging. While the fungi are doing all the legwork, the bacteria hitching a ride are busy growing and expanding.
This concerted action allowed the assemblages to rapidly form biofilms (dental plaque), sticky networks of microbes that can lead to tooth decay and gum disease.
The bacterial-fungal clusters were also more resistant to antimicrobial agents commonly used in mouthwash and tougher to rinse off tooth-like surfaces than either species alone. On pieces of real human teeth, the assemblages formed denser biofilms and caused more extensive enamel damage and decay.
The results could provide insights into prevention methods and treatments for tooth decay, which affects 42% of American children and 59% of adolescents aged 12-19, according to the National Institute of Dental and Craniofacial Research, which funded the study.

























